Arriving in Style
Plane and Pilot
FEBRUARY 28, 2025
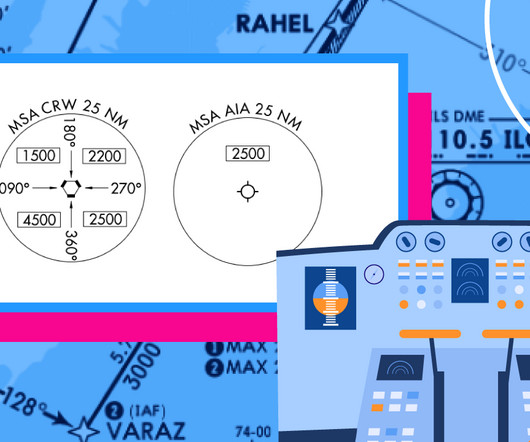
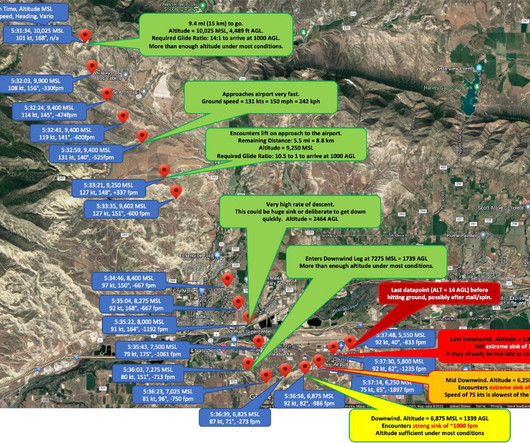
To cope with these challenges, airline glass flight decks contain a vertical navigation function (VNAV) that keeps the autopilot, and the crew, on the right path to arrive at the final approach fix, or downwind leg, at speed and on altitude. Both of these approaches work with one significant caution. When to Start Down?


















Let's personalize your content