Understanding Visual Flight Rules(VFR)
WayMan
MAY 2, 2024
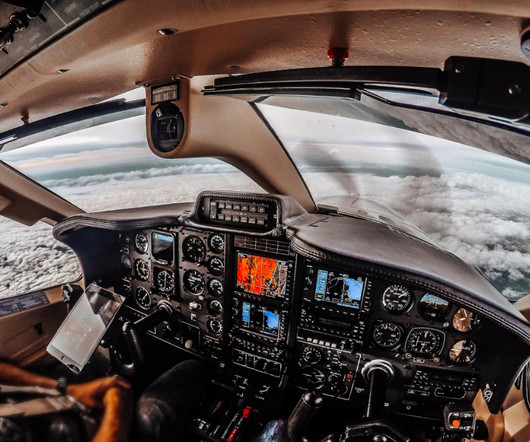
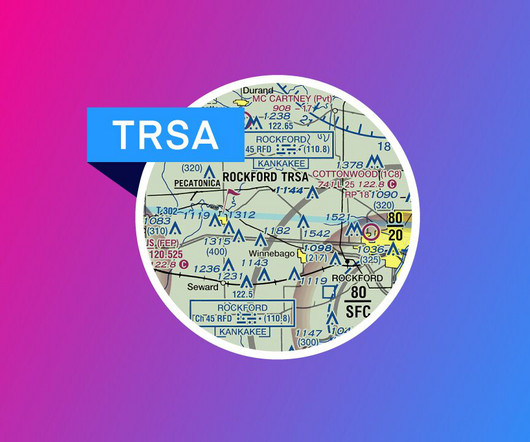
Visual Flight Rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Essentially, it allows pilots to operate the aircraft with visual references outside the cockpit.
















































Let's personalize your content