Delta Connection flight received sink rate alert before Toronto Pearson crash
Aerotime
MARCH 21, 2025
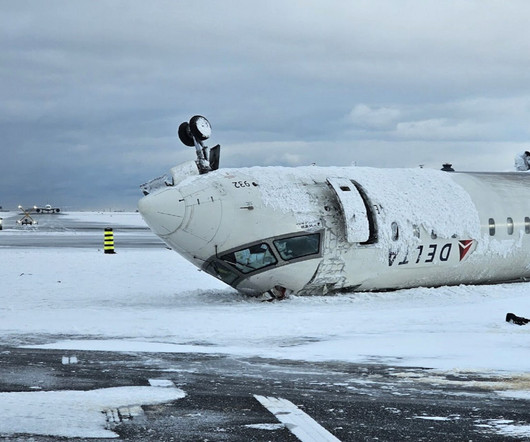
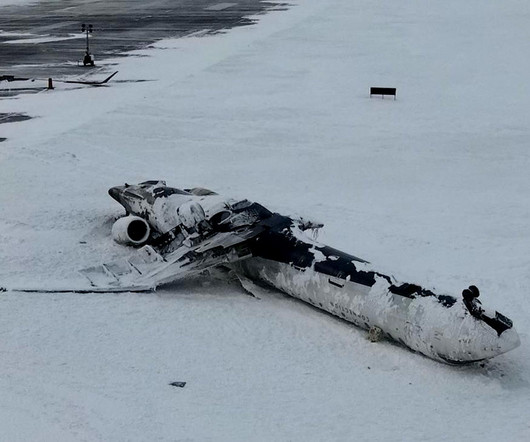
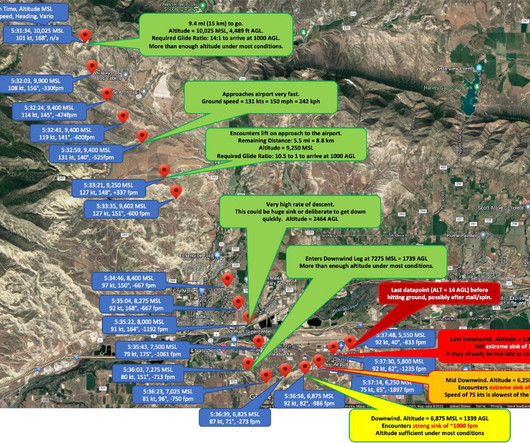
TSB Approach sequence Due to reported wind gusts as the CRJ900 approached Toronto Pearson following a flight from MinneapolisSaint Paul International Airport (MSP) the aircraft was flown at 149 knots. One second later (2.6seconds before touchdown), the EGPWS alert sink rate sounded, indicating a high rate of descent.
















Let's personalize your content