Classic Theory Meets Digital Computer; Status Quo Emerges Unscathed
Flying Magazine
MAY 7, 2025
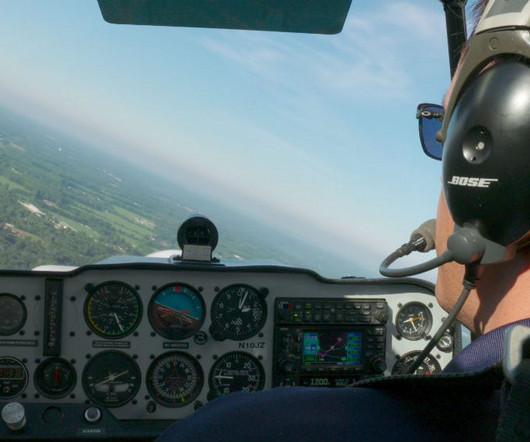
For instance, in the range of cruising power settings the specific fuel consumption of my Continental TSIO-360the rate of fuel flow required to generate one horsepowerimproves by about 1 percent with each increase in speed of three knots. Again, these are indicated airspeeds. mpg drops to 10.5.





































Let's personalize your content