How Exactly Does Reverse Thrust On A Plane Work?
Simple Flying
APRIL 5, 2025
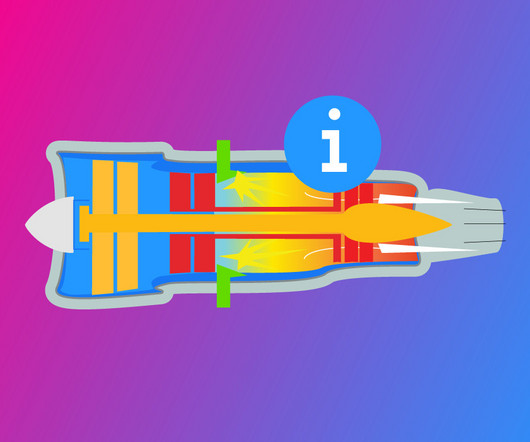
While brakes and aerodynamic drag contribute significantly to this process, another critical component is reverse thrust. In this article, we explore the origins, technical workings, and variations of reverse thrust systems , shedding light on how this essential technology operates in different types of aircraft.















































Let's personalize your content