Wingtip Vortices and Wake Turbulence
Pilot Institute
MARCH 28, 2025
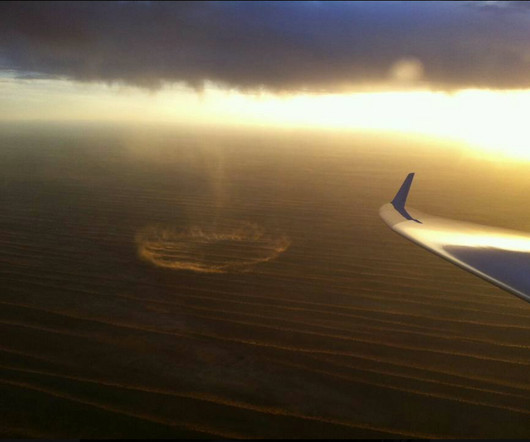
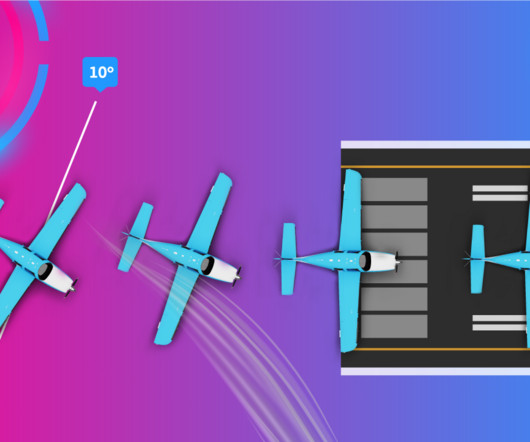
As seen from the aircrafts tail, the vortex rotates in the anti-clockwise direction on the right wingtip and the clockwise direction on the left wingtip. This horizontal component of lift is called Induced Drag. Its called induced drag since it only exists as a consequence of lift. Increased Drag Moving air around is hard work!






























Let's personalize your content