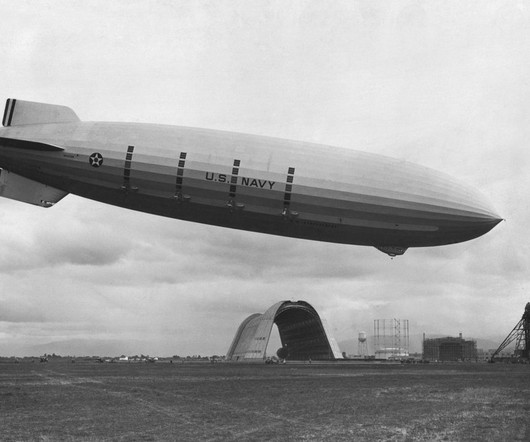
Today in Aviation History: Loss of USS Macon
Vintage Aviation News
FEBRUARY 12, 2025
The airship initially recovered, dumping ballast and stabilizing at 700 feet above the sea and returning to its cruising altitude of 1,600 feet, but the ship was sent into another plunge, falling a rate of 14 feet per second tail-down. Then, off Big Sur, near Monterey Bay, the USS Macon was caught in a storm.











Let's personalize your content