Crosswind Landing Gone Wrong: TUI Boeing 737 at Leeds Bradford
Fear of Landing
FEBRUARY 7, 2025
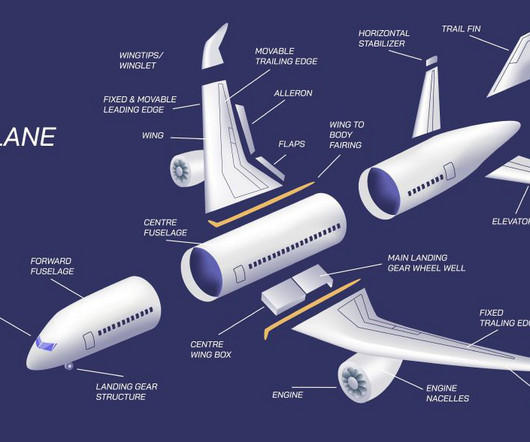
Just before touchdown, the captain used right rudder to “de-crab” the aircraft and landed smoothly in the touchdown area. The autobrake engaged, reverse thrust was deployed and they began to decelerate. As they decelerated, the captain reduced the right rudder to neutral. right rudder.






















Let's personalize your content