Learning Aeronautical Engineering From Historic Aircraft Designs
Vintage Aviation News
APRIL 1, 2025
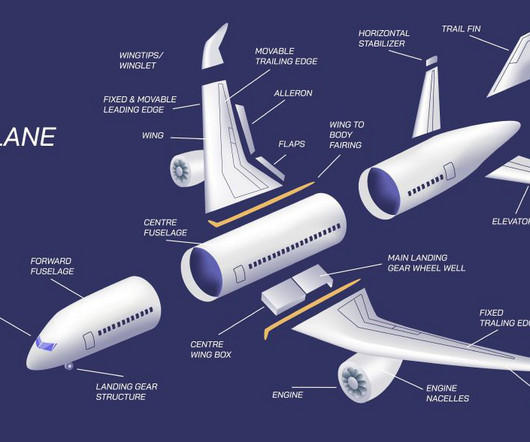
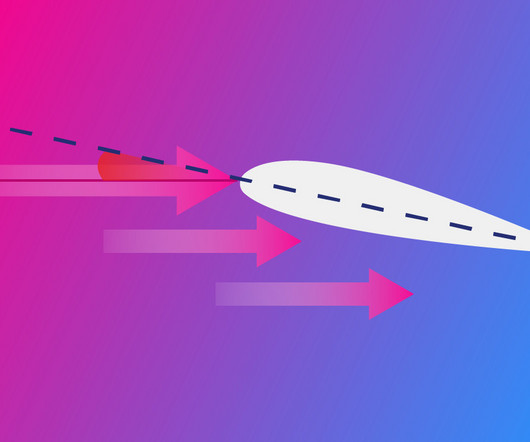
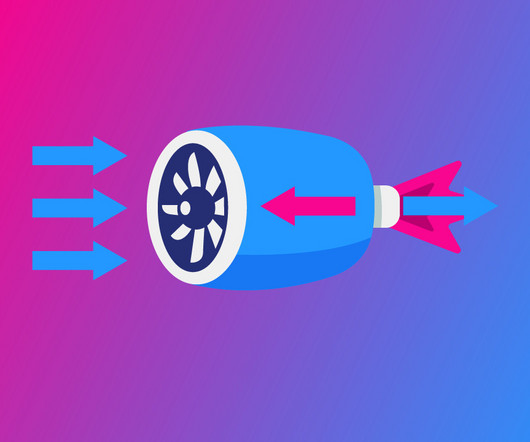
Studying historical aircraft helps students understand the development of flight and learn from early engineers about problems of lift, propulsion, stability, and material constraints. Often touted as the first successful powered aircraft, the Wright Flyer (1903) clearly shows lift, propulsion, and control.































Let's personalize your content