The Unfulfilled Promise of the Fairchild T-46
Flying Magazine
MAY 14, 2024
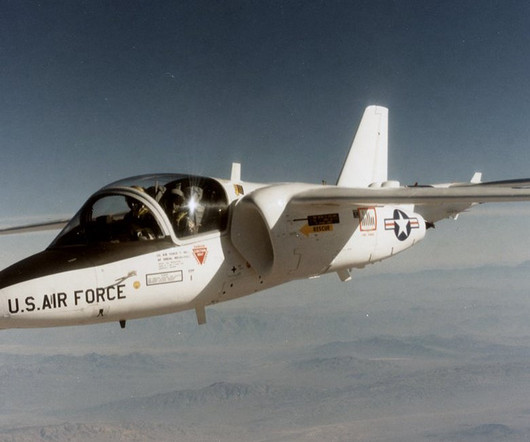
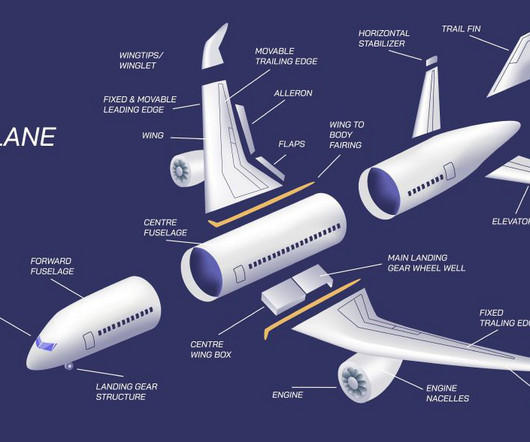
The most significant visual differences were the T-46’s high wing and the “H” tail, with twin vertical stabilizers mounted to the ends of the horizontal stabilizer that strongly resembled those of the company’s previous jet, the A-10 Thunderbolt II. As outlined in a U.S.













Let's personalize your content