Delta Connection flight received sink rate alert before Toronto Pearson crash
Aerotime
MARCH 21, 2025
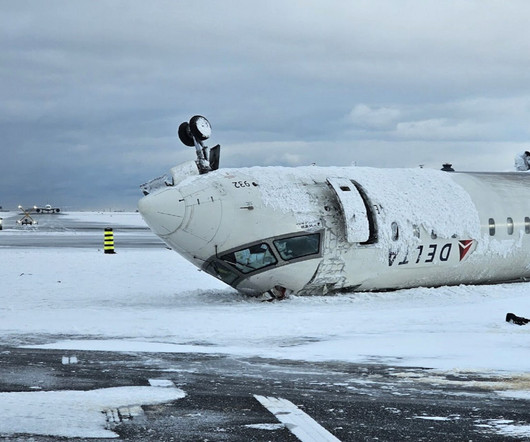
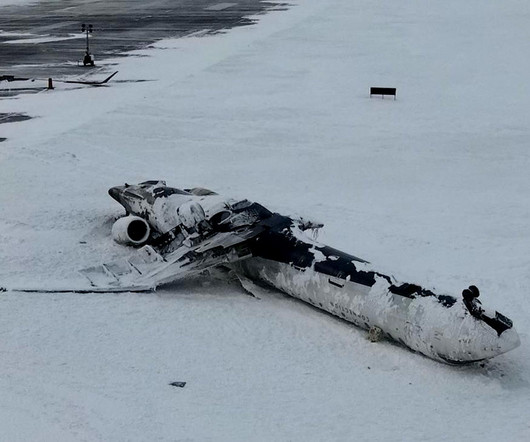
While the report draws no conclusions as to the cause of the crash, investigators set out a detailed timeline which focuses heavily on the Mitsubishi CRJ900s descent. The pilot flyingpulled back the thrust levers, and as a result, over the following 5seconds, N1 decreased from 64% to approximately 43%, where it remained until touchdown.


























Let's personalize your content