Examining over 100 years of flight automation and the history of the autopilot
Aerotime
APRIL 3, 2025
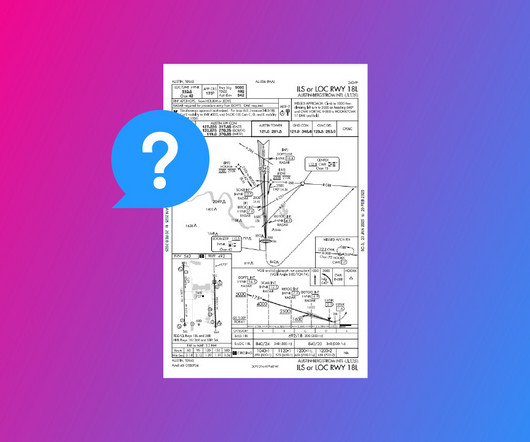
The 56 aircraft that participated in the 1914 competition presented a wide range of aviation innovations, ranging from assisted starting mechanisms, automatic carburetors, basic stabilization systems, and many other innovations that purported to benefit aviation safety.















































Let's personalize your content