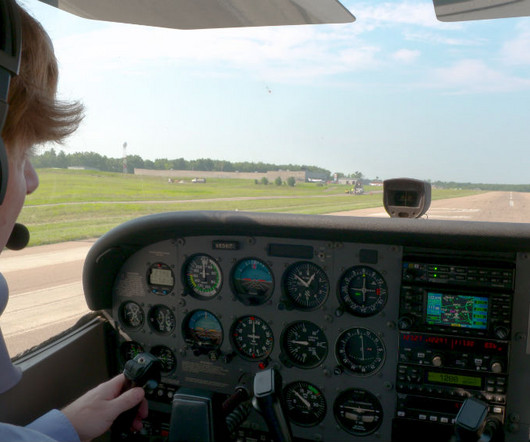
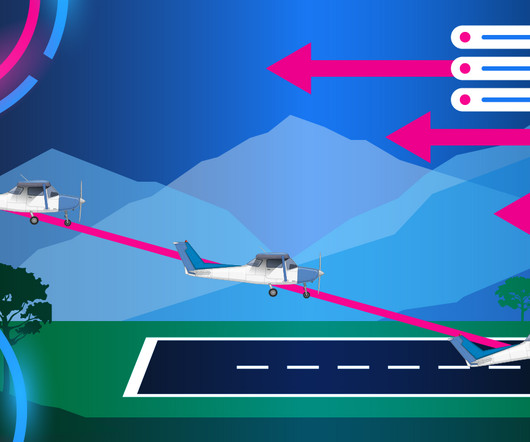
What Is Ground Effect?
Pilot Institute
OCTOBER 2, 2024
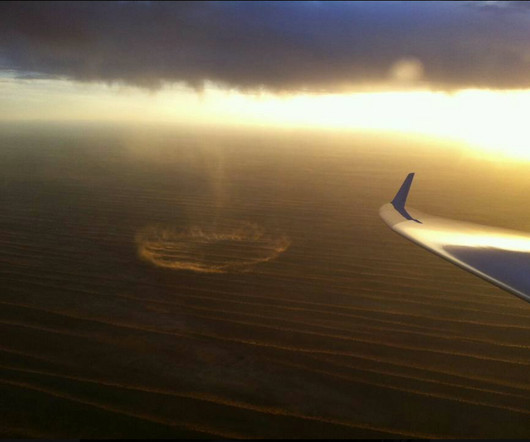
Your wings don’t create as much drag as they would at higher altitudes, which gives you extra lift. Key Takeaways Ground effect increases an aircraft’s lift and decreases drag. Lift increases due to the high-pressure area created by the compressed air beneath the wings. In-Ground-Effect vs.












Let's personalize your content