How to Read a Windsock
Pilot Institute
JANUARY 3, 2025
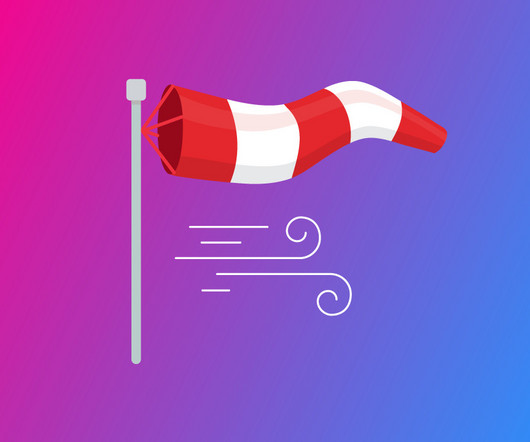
A windsock can become your main source of real-time wind information, especially when your aircraft radio equipment is unavailable or malfunctions. More Safety Private Pilots usually fly lighter aircraft that are more sensitive to wind. These aircraft have lower crosswind limitations and are more affected by gusts and wind shear.




















Let's personalize your content