Quick Crosswind Calculation for Pilots
Pilot Institute
APRIL 5, 2025
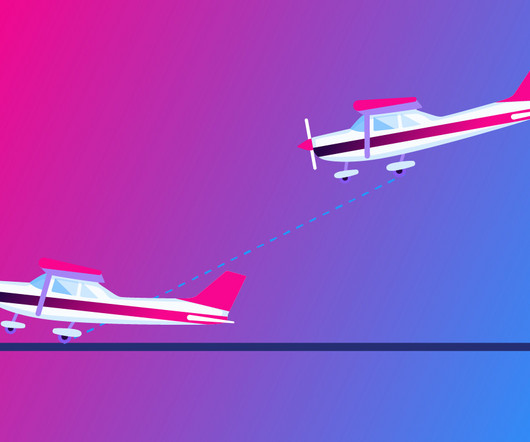
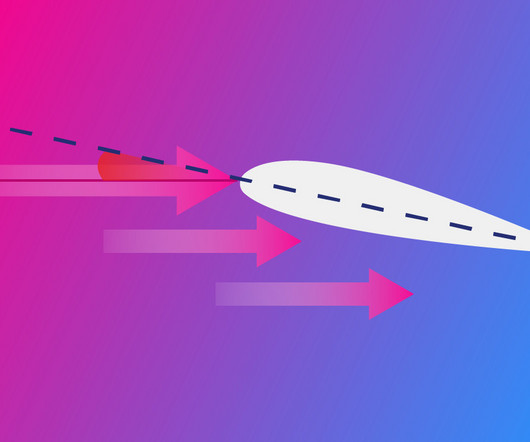
In this article well demonstrate how to perform a quick crosswind calculation and why it is important to know. Key Takeaways Crosswinds are nearly always present Knowing how to calculate them is essential for safe flying. Use the clock face method A simple way to estimate crosswind components quickly. What Is a Crosswind?






























Let's personalize your content