Delta Connection flight received sink rate alert before Toronto Pearson crash
Aerotime
MARCH 21, 2025
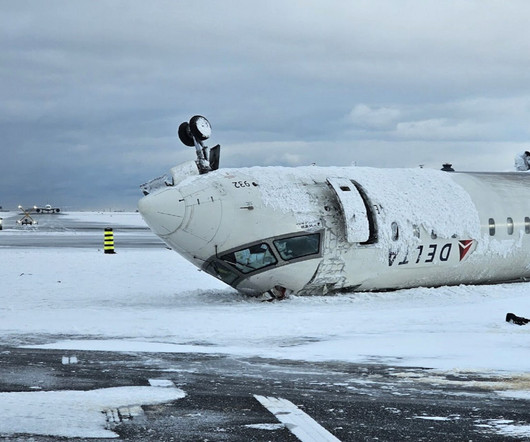
While the report draws no conclusions as to the cause of the crash, investigators set out a detailed timeline which focuses heavily on the Mitsubishi CRJ900s descent. TSB At a height of 50 feet the rate of descent had increased to 1114 feet per minute (fpm) from 672 fpm around 14 seconds before. to the right, the TSB said.





































Let's personalize your content