5 Most Common Aircraft Flap Types (Explained by a CFI)
Northstar VFR
MAY 26, 2025
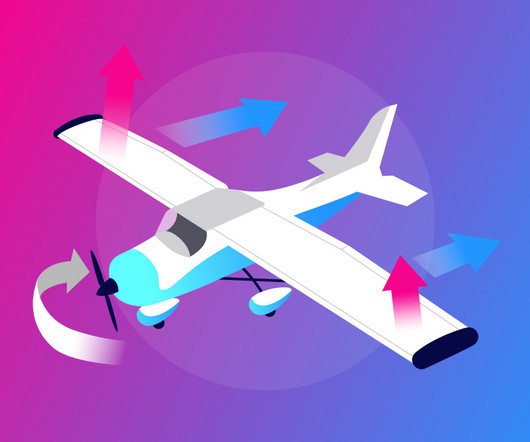
When deployed, they increase the wings lift and drag, allowing the airplane to fly safely at slower speeds. When flaps extend, they increase the camber (curvature) of the wing, which boosts the amount of lift the wing generates. On takeoff , flaps help the airplane become airborne sooner by increasing lift.



















Let's personalize your content