Examining over 100 years of flight automation and the history of the autopilot
Aerotime
APRIL 3, 2025
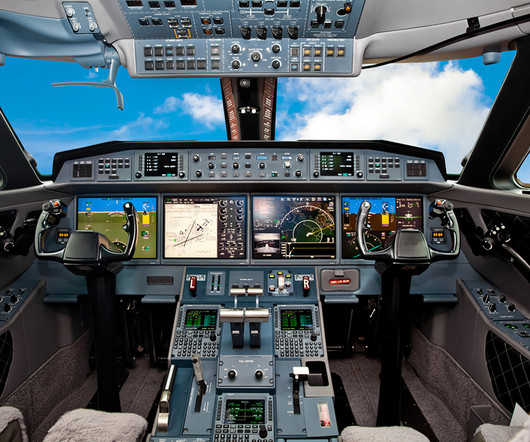
His system would provide an aircraft with automatic stability and control mechanism, through the control of the ailerons, stabilizer, and tail rudder through the use of a set of simple gyroscopes. The process of flight can be divided into seven crucial stages – taxi, take-off, climb, cruise, descent, approach, and landing phases.



























Let's personalize your content