Is a Waiver to Fly Drones in Controlled Airspace Still Necessary?
Pilot Institute
JUNE 27, 2025
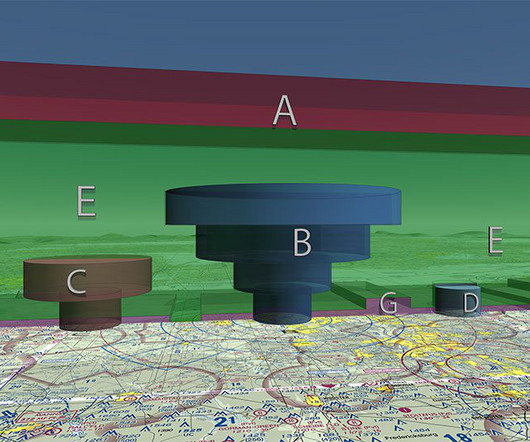
Know what special scenarios still require a waiver, such as flying BVLOS operations, flights above people, or flights that exceed the standard 400 feet AGL. Aircraft must operate under ATC clearance. Shelf area: 10 NM radius, from 1,200 ft AGL to 4,000 ft AGL. Ceiling is labeled in brackets within the airspace.
























Let's personalize your content