FAA Transponder Requirements Explained
Pilot Institute
DECEMBER 27, 2024
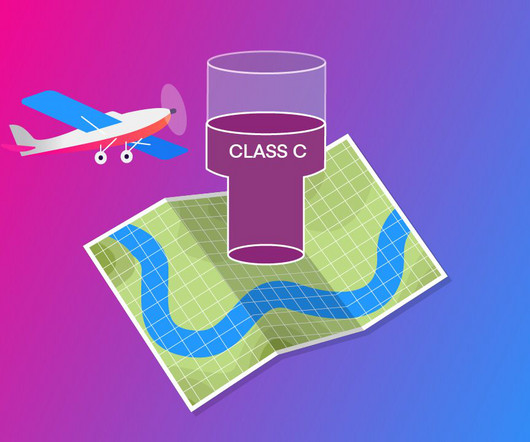
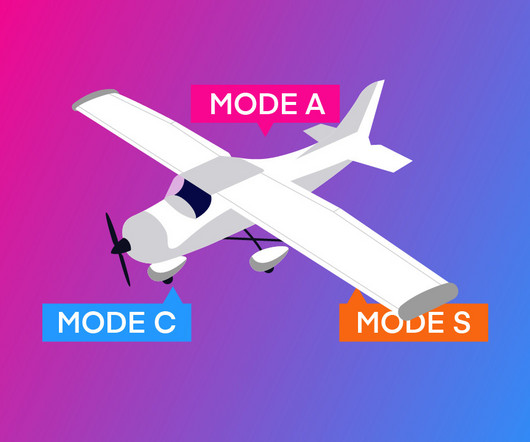
A transponder is not required unless an aircraft is operating: In Class A, Class B, or Class C airspace. Above 10,000 feet Mean Sea Level (MSL), excluding airspace below 2,500 feet Above Ground Level (AGL). Above, and within the lateral boundaries of Class B or Class C airspace up to 10,000 feet MSL.













Let's personalize your content