Radio calls during power off 360 at NTA
Ask a Flight Instructor
JANUARY 26, 2025
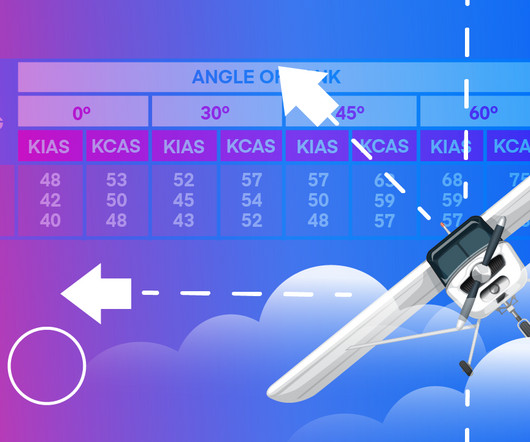
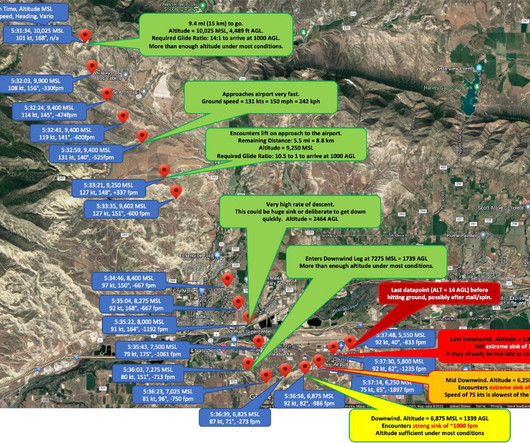
I typically arrive over the airfield/intended landing point 3,000 AGL then fly a 360 degree steep descent to a short final. I believe the civilian equivalent is the 360 degree power-off landing once required of commercial pilot candidates, and described in previous editions of the Airplane Flying Handbook.




























Let's personalize your content