Demonstration Stalls
CFI Academy
MARCH 28, 2025
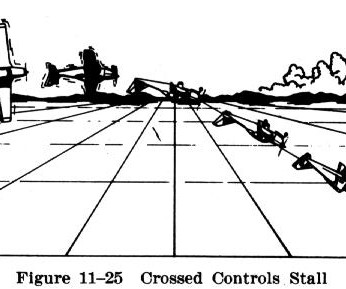
Heres what they are and what you need to understand about each: Crossed-Control Stall What It Is: This stall occurs when the aircraft is in a skidding turn, typically with ailerons applied in one direction and rudder in the opposite direction (e.g., left aileron, right rudder). How to Perform: Enter a turn (e.g.,












Let's personalize your content