Understanding the FAA’s DROTAM
CFI Academy
MARCH 5, 2025
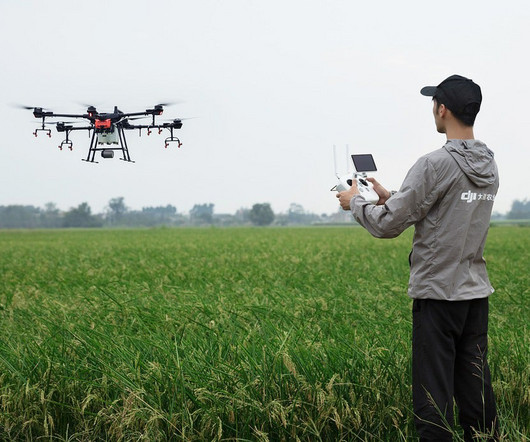
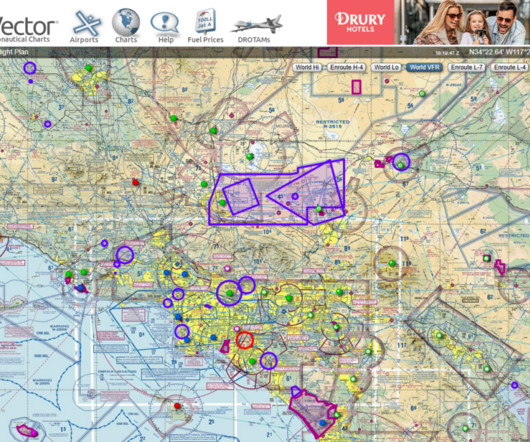
They notify you when and where drone operatorsthink utility companies or filmmakersare flying, typically at low altitudes (below 400 feet AGL). For example, a DROTAM might read: UAS activity within 1 NM of 39.1234N/076.5678W, 200 ft AGL, 0800-1700 local. We do get occasional DROTAMs here, which are usually for upto 400′ AGL.







































Let's personalize your content