Demonstration Stalls
CFI Academy
MARCH 28, 2025
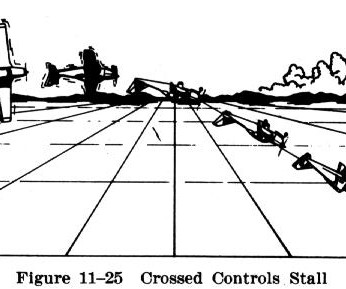
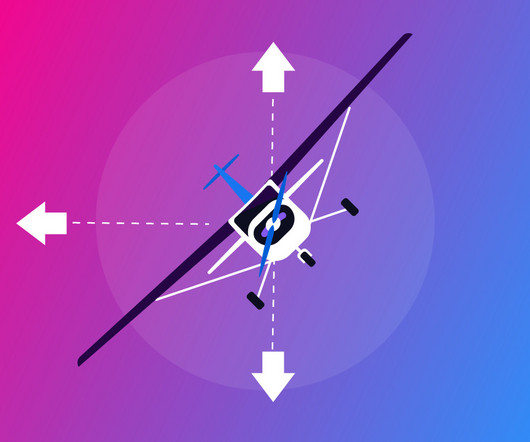
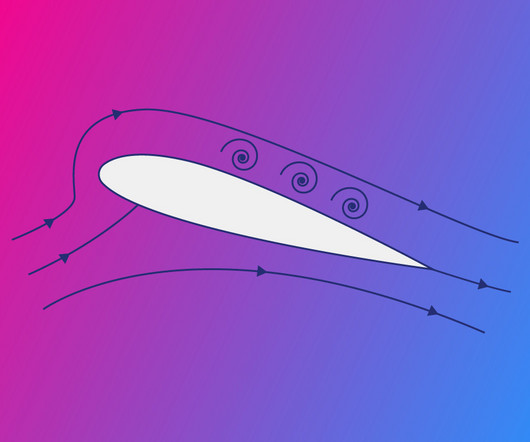
These stalls are outlined in the FAA’s Airman Certification Standards (ACS) for Flight Instructor – Airplane (effective May 31, 2024, replacing the older Practical Test Standards, or PTS). There are indeed four demonstration stalls youll need to master for the CFI checkride. left aileron, right rudder).









Let's personalize your content